Datapoint type, master datapoint and datapoints
As mentioned in the introduction, the master datapoint is the central element in mass configuration. This page aims to provide essential information on creating and configuring a master datapoint for mass configuration.
One or more datapoints are created in the database of the WinCC OA system on the basis of the master datapoint. All configuration settings for the master datapoint are transferred to a new datapoint when it is created. Subsequent changes to the master datapoint are transferred automatically to datapoints at runtime. If PowerConfigs containing dynamic attributes are added to the master datapoint, then changing a dynamic attribute does not result in this change being adopted by existing datapoints. Settings for dynamic attributes must be made using PowerConfig configuration at the datapoint.
Before you can create a master datapoint or datapoint at all, a datapoint type must be defined specifying the structure and data types of the leaf elements. The chapter PARA/Create a datapoint type contains further information on creating a datapoint type.
The renaming of a datapoint type or node in the structure, with presence of a master datapoint, is not supported by the Dp-Type-Editor. Since the name of the master data point consists of the datapoint type name (see below), the mass configuration would not work anymore in case of changing the type name! The changing of the datapoint type structure (insert, delete node) can be performed at any time.
Once you have defined the structure of your datapoint by creating a datapoint type, your next step can be to add the master datapoint. To do this, right-click on a data point type and select the option Create master datapoint in the context menu that opens.
The figure below shows the context menu:

The name given to the master datapoint is constructed as _mp_ + datapoint type name. A gray folder symbol with a red point on the left side below, indicates a master datapoint in the PARA module.
Of course it is not an essential requirement to create a master datapoint. After defining a datapoint type you can create just one datapoint (see also Creating a datapoint) or multiple datapoints (see also Creating multiple data points).
The major drawback in creating multiple datapoints without an existing master datapoint is that changes are not transferred to all the datapoints (apart from those made at the datapoint type itself). Thus each datapoint would need to be provided with configs and configured individually. Another disadvantage is that it is also not possible to work with PowerConfigs if there is no master datapoint. By inserting a PowerConfig (for example, alert handling with 3 ranges) at the datapoint element of the master DP, the configured settings are transferred to all existing datapoints (only dynamic attributes can be changed). If the master datapoint is subsequently deleted, the "alert handling" Config can then be changed in any way for each datapoint (ranges, limits and alert classes can be configured to suit). When a new master DP is created, this contains no alert-handling Config. Re-inserting a PowerConfig for alert handling, and setting the parameters in the master DP, once again transfers the settings to all the DPs, so that the parameters changed previously on the individual DPs are lost. The user must be aware of this process and take care when deleting and creating a master datapoint in order to avoid producing inconsistencies in the project.
In order to guarantee that the mass configuration works properly and that there are no inconsistencies in the system the configs always have to be configured via the master datapoint. Afterwards the datapoints can be created. If the master datapoint is deleted or created when datapoints exist problems with the mass configuration and the already existing configs may occur!
When working with the mass configuration facility in WinCC OA, always use the functions/panels provided (Creating multiple datapoints, Deleting multiple data points, PowerConfig configuration, Templates/DP lists, Excel tools). Avoid making changes using CTRL scripts you have written yourself, external database tools, exporting and importing DP lists in standard format using the ASCII Manager or the like, as this can lead to inconsistent states in the system.
Define the master datapoint for a datapoint type and provide this with Configs (for more details of the datapoint Config refer to PARA Module/datapoint configs, basics) and PowerConfigs (more details in PowerConfigs, basics). Configure these Configs to suit your requirements. If multiple datapoints are created after configuration then these are derived from the master datapoint and have the same settings. Any changes to the master datapoint (for example, adding a Config, modifying the values set in a Config etc.) have the same effect on all datapoints of this type at runtime.
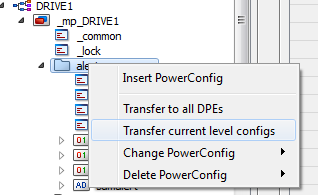
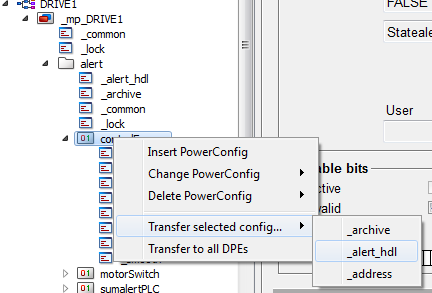
The Transfer to all DPEs option in the context menu of the master datapoint (right-click on the master datapoint) updates all datapoints with the configs and configurations set in the master datapoint. A confirmation prompt appears before the transfer is made to all DPEs, however. Use this function to maintain consistency in the system. Use the option "Transfer current level configs" (right-click on a datapoint node) to transfer the configs of the selectednode to all datapoints. All other elements are not changed. To transfer one selected config of an element, use the option "Transfer selected config" (right-click on a datapoint element). This specific config of an element is transferred to all datapoints.
 Example
Example
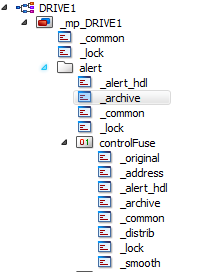
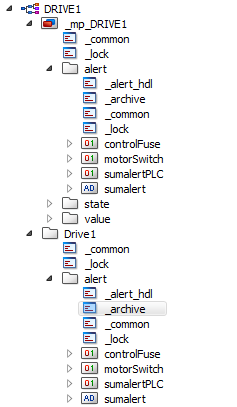
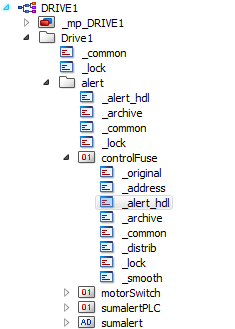
In the example below the "_archive" as well as the "_alert_hdl" configs of the "alert" node of the master datapoint _mp_DRIVE1 are transferred to the alert node of the "Drive1" datapoint by using the option "Transfer current level configs".
The configs _common and _lock are not transferred by using the option "Transfer current level configs".
 Example
Example
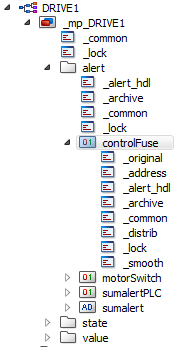
In the following example, the _alert_hdl config of the datapoint element "controlFuse" of the master datapoint _mp_DRIVE1 is transferred to the datapoint element "controlFuse" of the "Drive1" datapoint.
Old PARA Module
The PARA module has been provided with new functions for mass configuration (context menus, appearance of the tree structure). You can change back to the "old mode" at any time as follows:
- Open the panel <wincc_oa_path>/panels/para.pnl in GEDI.
- In the panel, click on the ActiveX object in the tree view and switch to the Events tab.
- Open the Initialize script.
- There are 2 comment lines in the middle of the script. Remove the two "//" from the second comment line and click on OK in the Script Editor.
- Save the panel and restart the PARA module.
The "old" PARA module is now available again (in this case mass configuration can no longer be used). It is necessary to change the PARA module if you have previously already used master datapoints and then want to use the functions of the earlier configuration module.



